TL;DR
- Low-Fidelity Prototypes: Quick sketches or wireframes for early idea validation.
- High-Fidelity Prototypes: Interactive, detailed designs for usability testing.
- Horizontal & Vertical Prototypes: Broad overview vs. focused functionality based on project needs.
- Rapid, Evolutionary & Throwaway Prototypes: Fast iterations, continuous improvement, or temporary mockups.
- Tools & Best Practices: Use Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch; gather user feedback, avoid overcomplication, and iterate.
Introduction
Prototyping is a crucial step in product development, helping startups and designers transform ideas into tangible solutions. With prototype development services, teams can quickly create visual or interactive models of their products to test usability, gather user feedback, and refine designs before full-scale development.
When combined with MVP development services, prototyping not only validates core features but also ensures that the minimum viable product meets market needs efficiently.
Whether you’re developing a software application, a web platform, or a physical product, leveraging these services reduces risks, saves development costs, and accelerates time-to-market allowing startups to launch smarter, faster, and with confidence.
Accelerate Your Prototype Development Today
Partner with experts to bring your ideas to life faster, test efficiently, and validate your product before full-scale development.

What is a Prototype?
A prototype is an early model of a product that showcases its main features and functionality. Unlike a final product, a prototype is designed to test ideas, gather user feedback, and refine designs before full-scale development. Prototyping helps startups and designers identify potential issues early, save time, and reduce development costs.
Prototype vs. MVP vs. PoC
- Prototype: Focuses on testing ideas and design concepts. It is not fully functional but helps validate the product concept.
- MVP (Minimum Viable Product): A working version of the product with core features to release to early users and collect real feedback.
- PoC (Proof of Concept): Validates whether a technical idea or solution is feasible before investing in full development.
Read More: PoC vs Prototype vs MVP: Key Differences Explained for Startup
Why Prototyping is Important
Prototyping plays a critical role in product development, especially for beginners and startups. It helps teams:
- Validate Ideas Early: Test concepts before full-scale development to avoid costly mistakes.
- Save Time and Resources: Identify potential issues early, reducing development effort and costs.
- Improve Team Communication: Provide a visual model that aligns designers, developers, and stakeholders.
- Enhance User Experience: Test functionality and usability to create products that truly meet user needs.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing a Prototyping Type
Selecting the right prototyping type is crucial for successful product development. Before deciding, consider these key factors:
- Project Goals: Are you validating a concept or testing detailed UX/UI elements?
- Complexity: Does your product require a simple interface or advanced functionality?
- Resources: Consider your budget, team skills, and the tools available for prototyping.
- Feedback Needs: How much user input do you need to refine the product effectively?
Choosing the right type of prototype ensures efficient development, better design decisions, and faster validation.
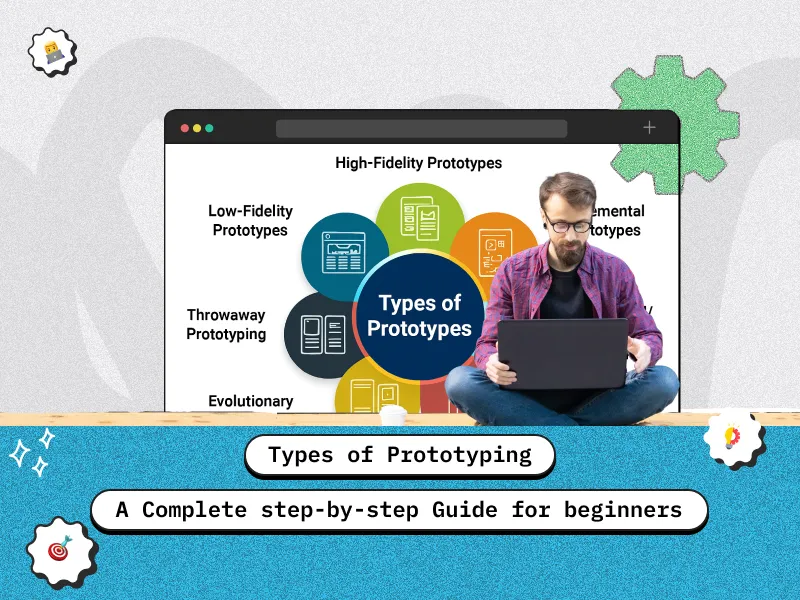
Types of Prototyping
Choosing the right type of prototype is critical for validating ideas, improving user experience, and reducing development costs. Here’s a detailed overview of the most common types of prototyping:
Low-Fidelity Prototypes
Low-fidelity prototypes are basic models of a product, often created using paper sketches, simple wireframes, or block diagrams. They are:
- Fast and inexpensive to create
- Ideal for early concept validation
- Useful for testing design ideas without heavy investment
These prototypes help teams quickly identify usability issues and refine layouts before moving to digital or interactive models.
High-Fidelity Prototypes
High-fidelity prototypes are interactive digital models that closely resemble the final product in design, functionality, and user experience. Key benefits include:
- Testing detailed UX/UI elements
- Conducting usability testing with realistic interactions
- Collecting more accurate user feedback
High-fidelity prototypes are particularly useful for startups and designers aiming to validate complex features and improve the final product.
Horizontal vs Vertical Prototyping
Prototypes can also be categorized based on their scope and depth:
- Horizontal Prototyping: Provides a broad overview of the product covering multiple features at a basic level.
- Vertical Prototyping: Focuses deeply on a single feature, showing detailed functionality and interactions.
Choosing between horizontal and vertical prototyping depends on your project goals—whether you want to validate multiple features quickly or test a specific functionality in detail.
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping emphasizes speed and efficiency. Using tools like Figma, Adobe XD, or Sketch, teams can:
- Quickly create interactive prototypes
- Iterate designs based on user feedback
- Accelerate time-to-market without compromising quality
This method is perfect for agile teams and startups that need to validate ideas fast and refine designs in real time.
Evolutionary Prototyping
Evolutionary prototyping is an iterative approach where the prototype is continuously refined and improved based on user feedback. Key advantages include:
- Adapting to changing requirements
- Improving usability and functionality over time
- Ensuring the final product aligns with user expectations and business goals
This approach is ideal for complex software and digital products that require ongoing improvement.
Throwaway / Rapid-Throwaway Prototyping
Throwaway prototyping is a method where quick mockups are created to validate ideas early, then discarded after testing. Benefits include:
- Quick validation of design concepts
- Reducing risk before full development
- Encouraging experimentation without heavy investment
This type is especially useful for startups or beginners who want to test multiple ideas without committing to detailed designs.
Choosing the Right Type of Prototype for Your Project
Selecting the right prototype ensures efficient development, accurate feedback, and cost savings. Consider these tips:
- Concept Stage: Use low-fidelity prototypes like sketches or wireframes. They are quick, inexpensive, and ideal for testing multiple ideas.
- Validation Stage: Use rapid prototypes to gather user feedback and refine designs. Tools like Figma or Adobe XD make the process fast and collaborative.
- Development Stage: Use high-fidelity or evolutionary prototypes for detailed UX/UI testing, realistic interactions, and stakeholder approvals.
For startups and businesses looking for expert support, partnering with Top Prototyping Companies can help accelerate product development, ensure professional-quality prototypes, and optimize the feedback and iteration process.
Calculate Your Development Costs Instantly
Use our Software Development Cost Calculator Tool to estimate your project budget and plan your prototyping and MVP development efficiently.

Tools and Software for Prototyping
Choosing the right tools can make prototyping faster, more efficient, and more effective. Here are some of the most popular prototyping tools for beginners and startups:
- Figma: A cloud-based, collaborative design tool perfect for UI/UX projects. Teams can design, prototype, and share in real time, making feedback and iteration seamless.
- Sketch: A vector-based design tool for Mac that is widely used for creating digital prototypes and interfaces. Ideal for designers focused on detailed UI layouts.
- Adobe XD: Offers interactive prototyping with animations and transitions, allowing teams to create realistic user experiences before development.
- InVision: A web-based prototyping platform that supports collaboration, feedback collection, and clickable prototypes, making it easy to share ideas with stakeholders.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Prototyping
Prototyping is a powerful tool, but beginners and startups often make avoidable mistakes. Here’s what to watch out for:
- Overcomplicating Early Prototypes: Keep early prototypes simple. Focus on core features instead of adding unnecessary details, which can slow down feedback and iterations.
- Ignoring User Feedback: Prototypes exist to gather insights. Neglecting user feedback can lead to misaligned designs and wasted development effort.
- Skipping Iteration Cycles: Iteration is key. Failing to refine prototypes based on testing can result in a product that doesn’t meet user expectations.
- Using the Wrong Prototyping Type for the Project Stage: Choosing a high-fidelity prototype too early or a low-fidelity prototype too late can reduce efficiency and increase development costs. Match the type to your project stage and goals.
Conclusion
Prototyping is a crucial step in turning ideas into successful products. By exploring different types of prototyping, beginners and startups can visualize concepts, test functionality, and gather feedback before full-scale development.
Using professional prototype development services ensures designs are thoroughly tested, while MVP development services help launch a product with core features quickly and validate market demand.
Adopting a structured prototyping approach helps reduce risks, save costs, and improve user experience. Start prototyping today to bring your ideas to life effectively.
FAQs:
1. What is prototyping in product development?
Prototyping is the process of creating an early model of a product to test ideas, gather feedback, and refine designs before full-scale development. It helps reduce risks and save costs.
2. What are the main types of prototyping?
The main types include low-fidelity, high-fidelity, horizontal, vertical, rapid, evolutionary, and throwaway prototypes, each serving different stages of product development.
3. How do I choose the right type of prototype?
Choose based on project stage, complexity, and feedback needs. Start with low-fidelity or rapid prototypes for idea validation, and use high-fidelity or evolutionary prototypes for detailed testing.
4. What are the benefits of prototyping for startups?
Prototyping helps startups validate ideas early, improve user experience, reduce development costs, and accelerate time-to-market. It ensures products align with user expectations.
5. Which tools are best for prototyping?
Popular tools include Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD, and InVision. These tools allow for interactive designs, collaborative feedback, and rapid iteration.
6. What common mistakes should I avoid in prototyping?
Avoid overcomplicating early prototypes, ignoring user feedback, skipping iteration cycles, and using the wrong prototype type for the project stage.
7. Can I use professional services for prototyping?
Yes! Prototype development services and MVP development services help startups and businesses create high-quality prototypes, validate concepts faster, and reduce development risks.










 30 mins free Consulting
30 mins free Consulting 
 10 min read
10 min read 


 Canada
Canada 
 Hong Kong
Hong Kong 
 Global
Global 





 Love we get from the world
Love we get from the world 